Backup/Restore MySQL database in linux
This document contains steps to perform backup and restore operations of AIV Database with MySQL database in linux platform.
References
Links usefull for backup and restore data are listed here,
https://devopsarticle.com/install-create-backup-restore-mysql-on-ubuntu-20-04-lts-6-easy-steps/
https://phoenixnap.com/kb/how-to-backup-restore-a-mysql-database
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-backup-mysql-databases-on-an-ubuntu-vps
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-mysql-on-ubuntu-20-04
There are 2 ways we can perform this,
Using terminal
MySQL Workbench application
1. Using terminal
Backup
List of commands used to perform backup and restore operation are listed below,
Skip the steps of installing & creating sample and backup database if you already have installed or created. continue from step 17.
Install MySQL by executing this command:
sudo apt install mysql-client
Check Installed MySQL version by running this command:
mysql -V
Install MySQL server by executing this command
sudo apt install mysql-server
In Ubuntu systems running MySQL 5.7 (and later versions), the root MySQL user is set to authenticate using the auth_socket plugin by default rather than with a password. This plugin requires that the name of the operating system user that invokes the MySQL client matches the name of the MySQL user specified in the command, so you must invoke mysql with sudo privileges to gain access to the root MySQL user:
sudo mysqlinfoIf you find wny error executing this command like ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock' (2) it might due to MySQL server is not running.
Execute this command to start MySQL server :
sudo service mysql startand try again.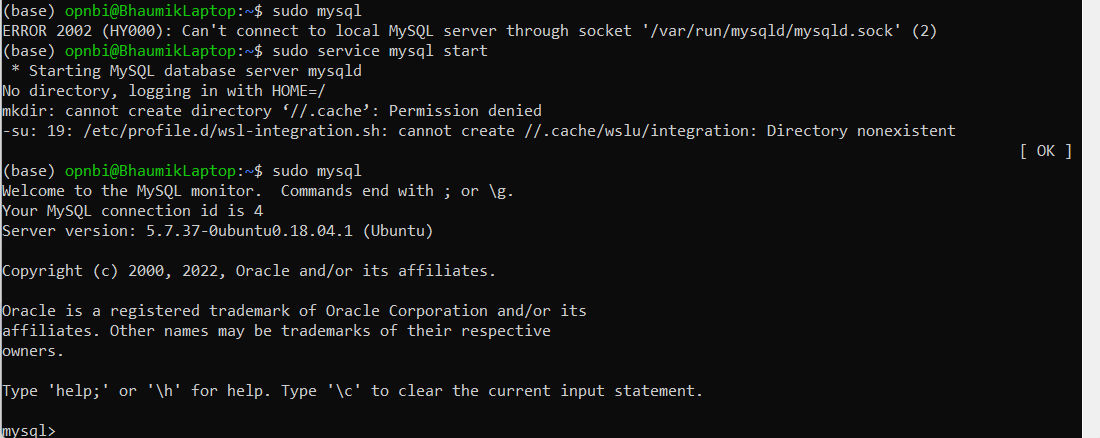
Once you have access to the MySQL prompt, you can create a new user with a CREATE USER statement. These follow this general syntax:
CREATE USER 'username'@'host' IDENTIFIED WITH authentication_plugin BY 'password';infoAfter CREATE USER, you specify a username. This is immediately followed by an @ sign and then the hostname from which this user will connect. If you only plan to access this user locally from your Ubuntu server, you can specify localhost. Wrapping both the username and host in single quotes isn’t always necessary, but doing so can help to prevent errors.
For example,
CREATE USER 'sammy'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Password@123';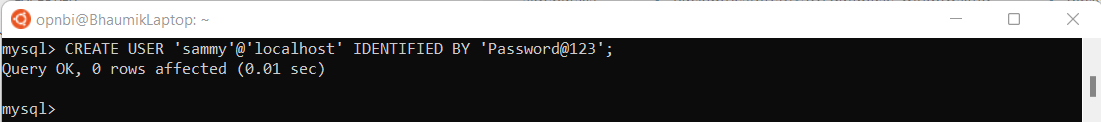
After creating your new user, you can grant them the appropriate privileges. The general syntax for granting user privileges is as follows:
GRANT CREATE, ALTER, DROP, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, REFERENCES, RELOAD on *.* TO 'sammy'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;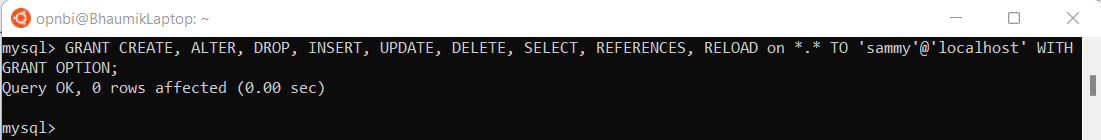
Following this, it’s good practice to run the FLUSH PRIVILEGES command. This will free up any memory that the server cached as a result of the preceding CREATE USER and GRANT statements:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Exit from mysql login:
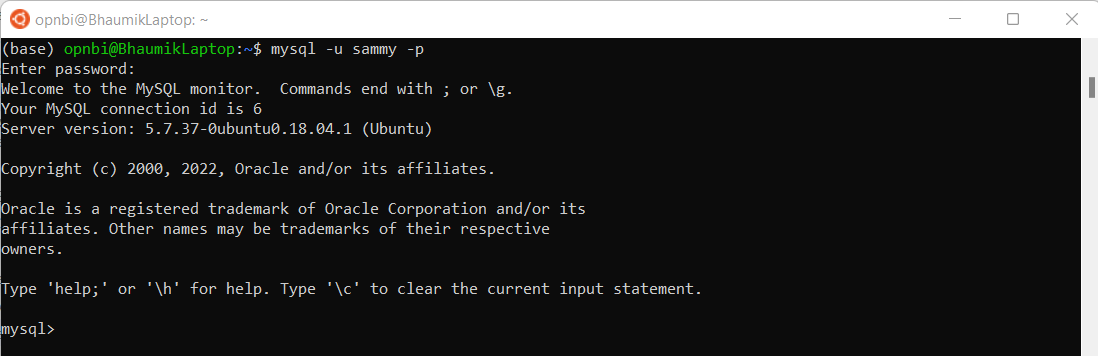
exitinfoIn the future, to log in as your new MySQL user, you’d use a command like the following:
mysql -u sammy -pEnter password you have provided instep No 5 and hit enter
Start MySQL server by running this command:
sudo service mysql start
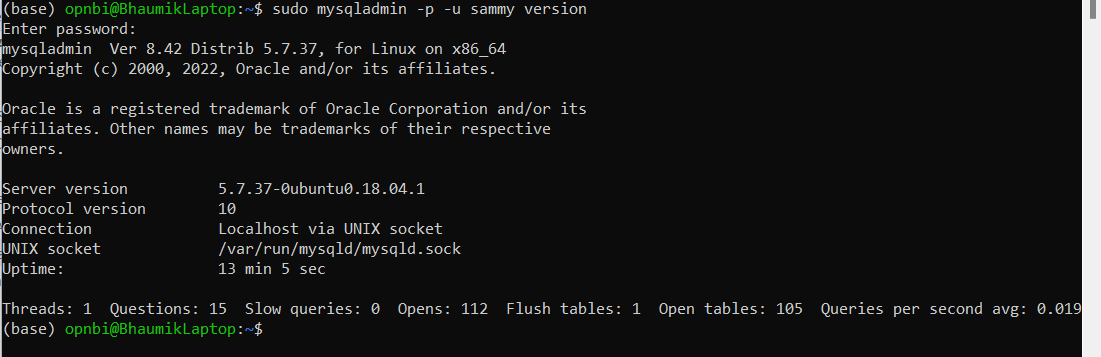
Check MySQL server version by executing below command,
sudo mysqladmin -p -u sammy versionEnter password you have applied for created user sammy in Step No 5.
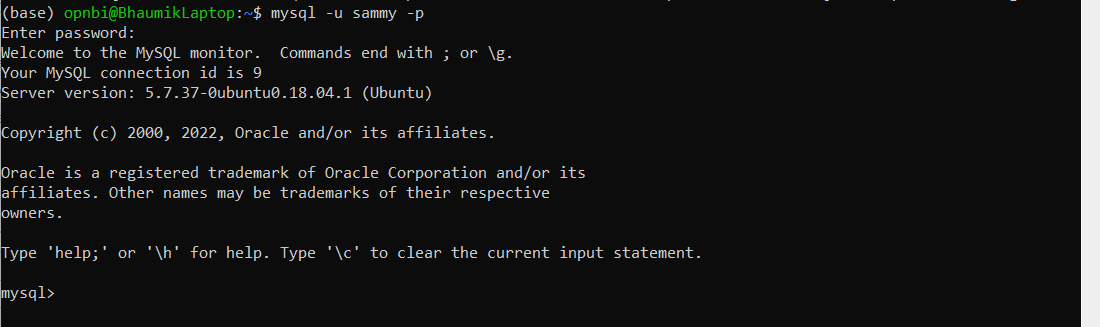
Connect with MySQL user, created in Step No 5 by running this command:
mysql -u sammy -pEnter password you have applied for created user sammy in Step No 5.
Once connected, execute this command to create database:
CREATE DATABASE sample_data;Switch to sample database created by executing this command:
USE sample_data;Execute this query to create sample table,
CREATE TABLE Persons (
PersonID int,
LastName varchar(255),
FirstName varchar(255),
Address varchar(255),
City varchar(255)
);
Insert sample data in to this created table by writing below query,
INSERT INTO Persons (PersonID, LastName, FirstName, Address, City)
VALUES ('2267', 'Erichsen', 'Jhon', 'Stavanger','Norway'),('2268', 'west', 'Allen', 'Central City','New York');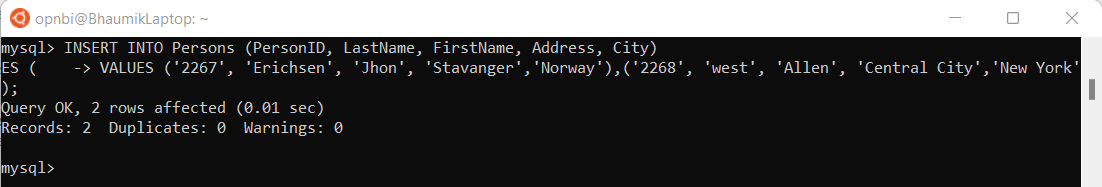
Disconnect from mysql user by writing :
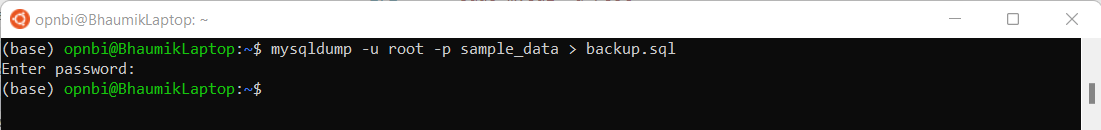
exitcommandExecute this command to take backup of sample_data database :
mysqldump -u root -p sample_data > backup.sqlinfoHere sample_data is database name of which we are taking backup and backup.sql is the backup file name which will be generated.
TipIf you are facing error like mysqldump: Got error: 1698: Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' when trying to connect
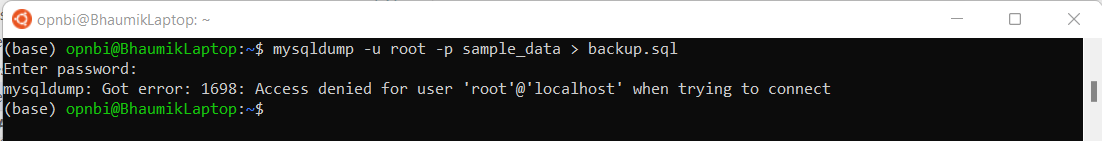
while executing this command, you need to reset password of root user. do this by executing this command,
sudo mysql -u root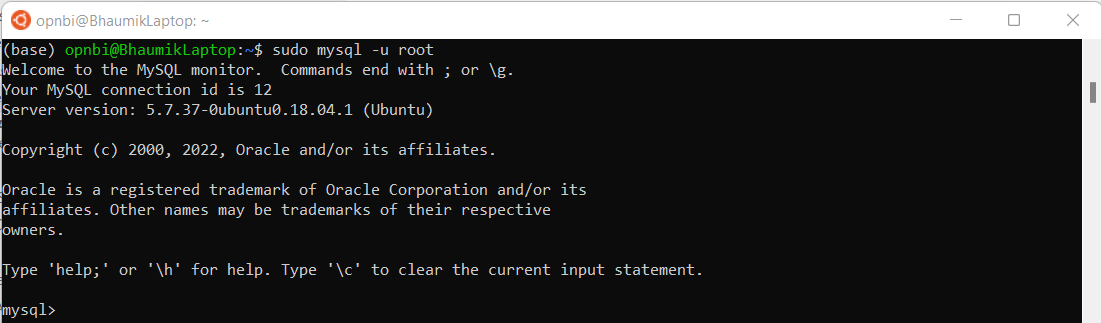
and then
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'new_password_here';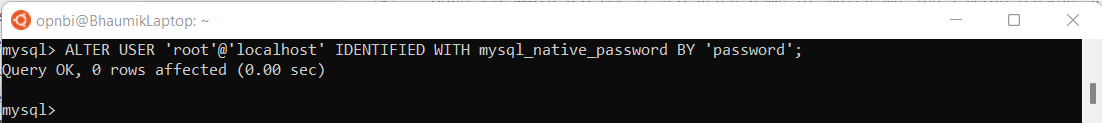
Now Exit from mysql server using :
ExitcommandExecute Step No 18 Command again and this time provide updated password for root user and it will work.
Check backup.sql file created in your system execute
lscommand
Restore
Follow this steps to restore backup file (.sql) file in MySQL database.
To restore data in new database, first let us create new database. login to mysql,
mysql -P 3306 --protocol=tcp -u root -pEnter password for root user and hit enter.
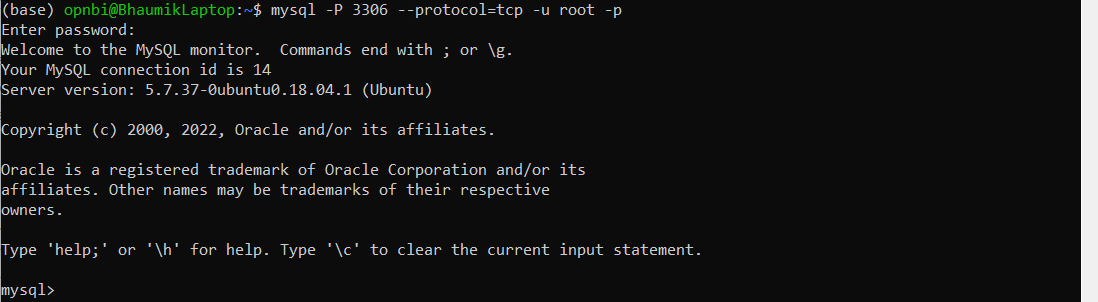
create new backup database
CREATE DATABASE restore_data;. here restore_data is name of database.
Exit from database by writing
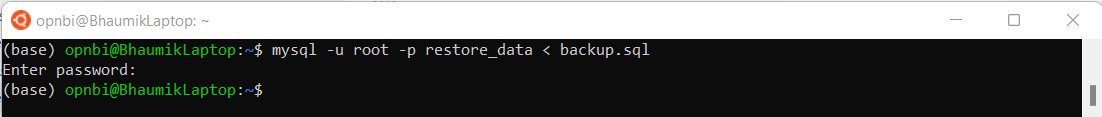
exitExecute this command to restore backup.sql file in restore_data database.
mysql -u root -p restore_data < backup.sqlEnter password for root user and hit enter
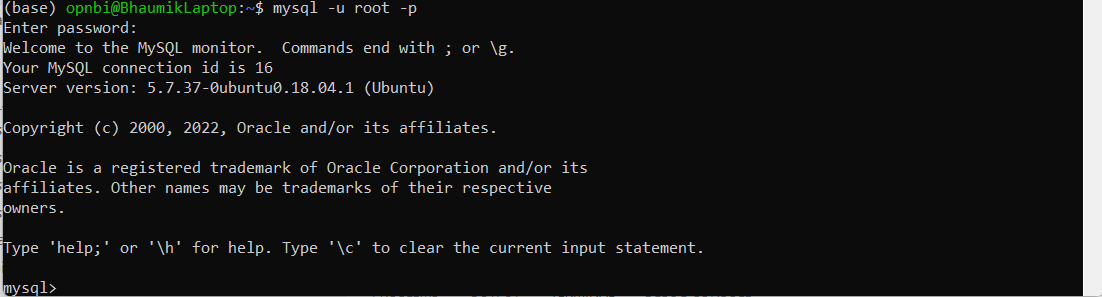
To check backup file restored or not, Connect with MySQL database:
mysql -u root -pEnter password for root user and hit enter
Change database to restore_data :
Use restore_data;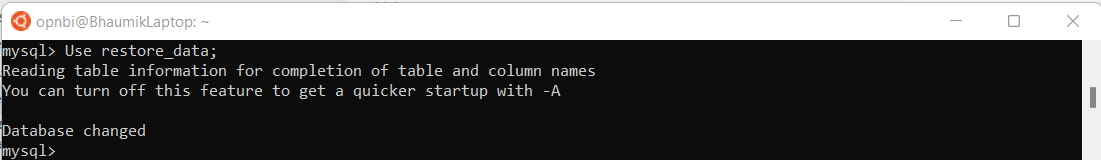
Run this query to fetch data from table,
select * from Persons;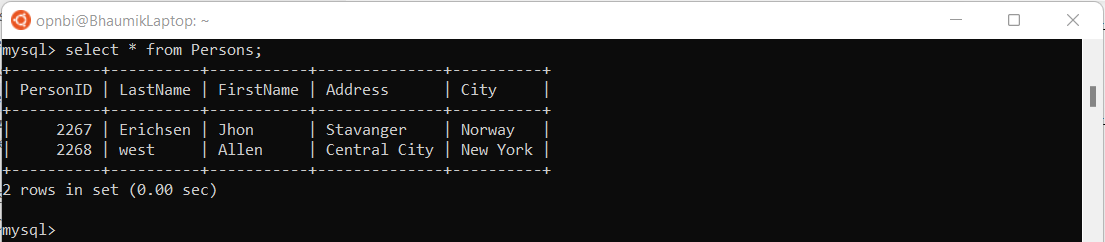
2. MySQL Workbench application
For Backup and restore database using self-contained file [.sql] please follow steps provided in below link,
For Docker User
Skip step no 1 to 11 if you have MySQL Database installed in your docker. connect with docker using command given in step no 4 and continue with step no 12.
Pull MySQL image in docker by executing this command in powershell:
docker pull mysql/mysql-server:latestor direclty fetch mysql image and run using command given in step 2.Run MySQL image by executing this command :
docker run --name backup-mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=1234 -d mysql:latestNotewhere some-mysql is the name you want to assign to your container, my-secret-pw is the password to be set for the MySQL root user and tag is the tag specifying the MySQL version you want. See the list above for relevant tags.
infoThis will run mysql if proper name of mysql image is provided,if not found any image it will download new image automatically. so use this command directly if you do not have mysql image downloaded.
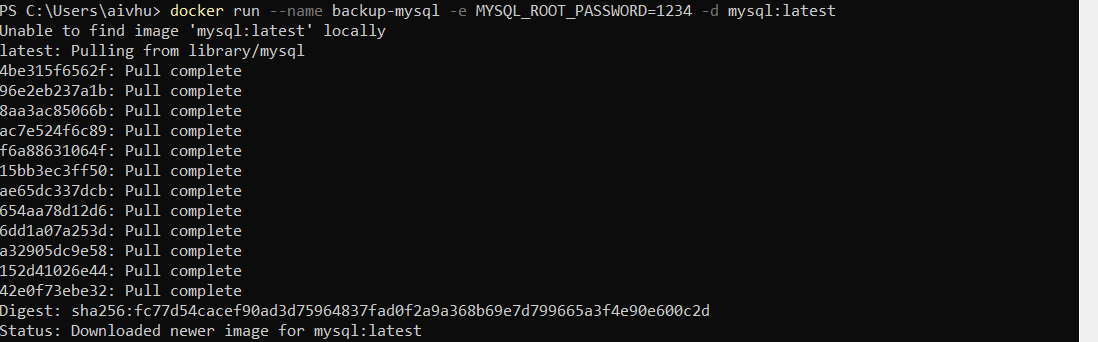
Get the list if docker images for MySQL
docker psyou will see container ID as gievn in below code,
Connect with MySQL containerID
docker exec -it 3680d544408d bashConnect with MySQL database by executing this command :
mysql -P 3306 --protocol=tcp -u root -pProvide password which you have applied in step 2 command and hit enter. Now you're connected to MySQL running in your container
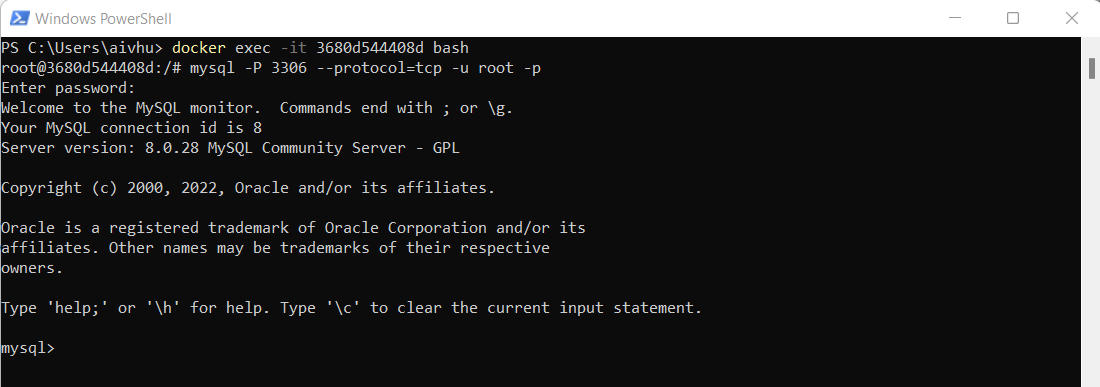
Check the list of database available by default in MySQL by executing this command:
SHOW DATABASES;Create new database in order to perform backup and restore operation :
CREATE DATABASE sample_data;infoIf you have your database then skip this step
Connect with created database to create sample tables inside it. execute this command:
USE sample_data;Now you are connected with sample_data database. to create a sample table execute this query,
infoIf you have own table and data, you can create table accordingly. This query is for demonstration only. if you have data tables created then skip this step
CREATE TABLE Persons (
PersonID int,
LastName varchar(255),
FirstName varchar(255),
Address varchar(255),
City varchar(255)
);
Once table is created, add a sample data in to this table bby executing below query,
infoIf you have database created, skip this step.
INSERT INTO Persons (PersonID, LastName, FirstName, Address, City)
VALUES ('2267', 'Erichsen', 'Jhon', 'Stavanger','Norway'),('2268', 'west', 'Allen', 'Central City','New York');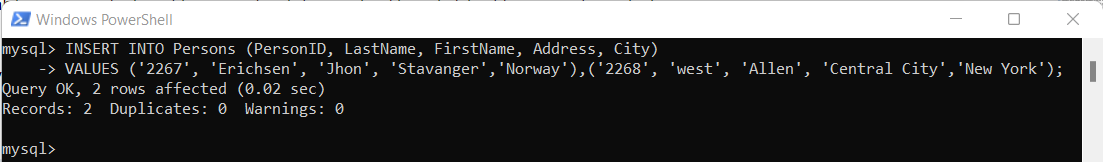
Once table is created, let's execute command to take backup of database. to do that you need to exit from mysql by executing exit command
execute this command from root user:
mysqldump -u root -p sample_data > backup.sqlOn successfull completion of above command check backup file is created or not execute this command:
ls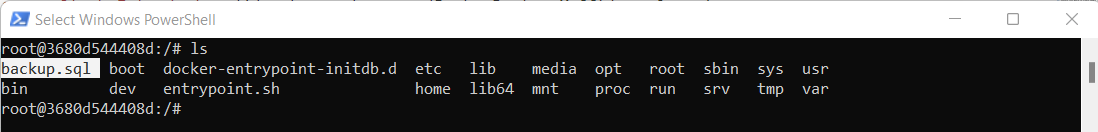 danger
dangerIf you already have backup database then skip step no 15 & 16. you can continue with step no 17
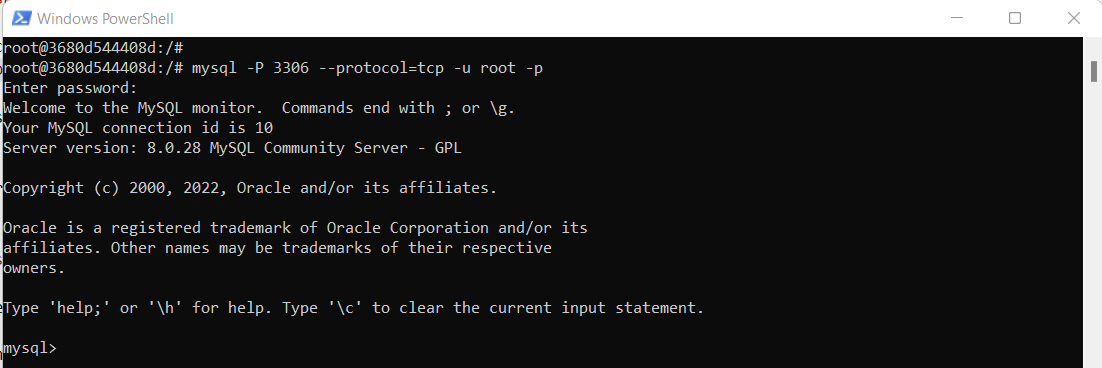
To backup data in new database, first let us create new database. login to mysql using
mysql -P 3306 --protocol=tcp -u root -pEnter password and hit enter
infoIf you already have backup database created, skip this step
Create new backup database :
CREATE DATABASE restore_data;Disconnect from MySQL database execute:
exitRestore from backup file execute this command:
mysql -u root -p restore_data < backup.sql. Enter password and it will work
To check database is restored or not login to MySQL:
mysql -u root -p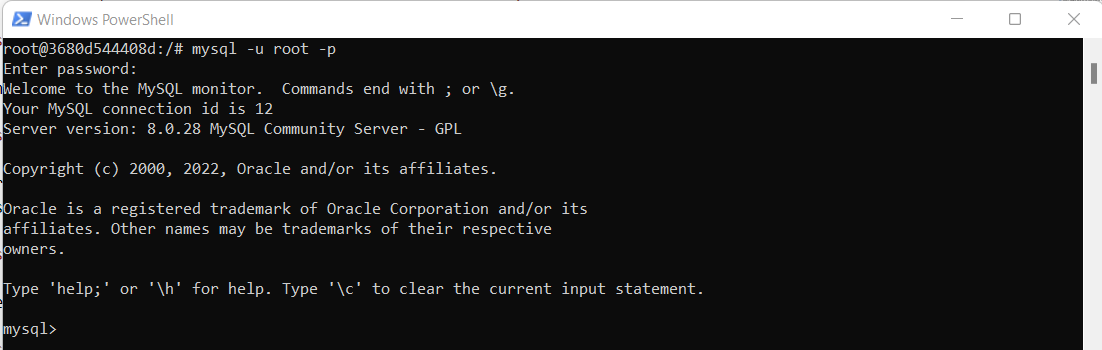
Connect with restore_data database Use:
Use restore_data;
Execute this query to get the table data:
select * from Persons;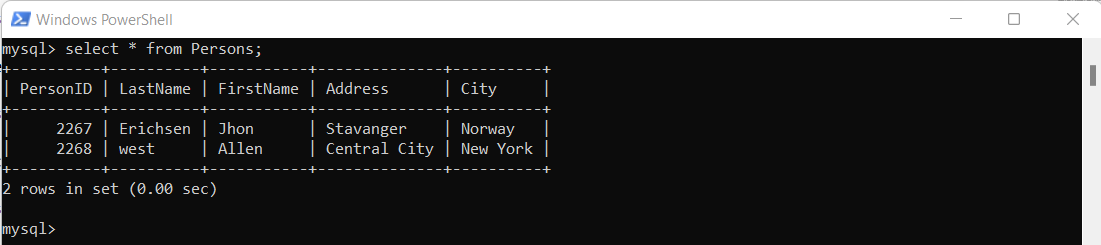
If your database is restored, you will get table data as output. you have successfully backup and restored MySQL database.